用vue开发也三周了,边学习边用,好在之前用过react能快速的看文档应付项目。
暂时还没有看过vue源码,本篇仅记录应用型测试了解生命周期各种钩子函数,更好的控制数据流和其对DOM的影响。
基础代码:
1 | <template> |
1 | <script> |
结果:
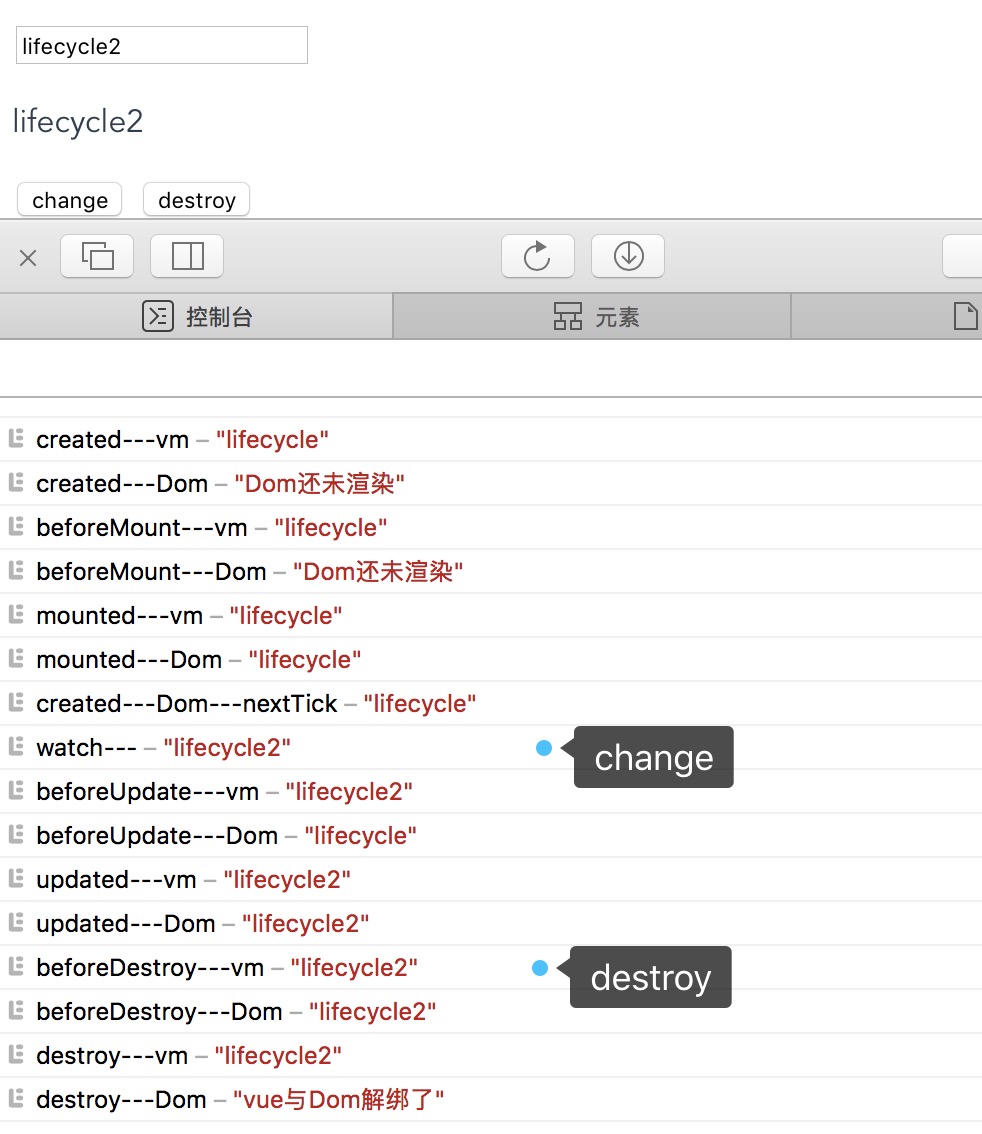
说明:
createdvue实例创建完毕,监测数据、初始化事件等等,此阶段能访问vue数据,不能访问到DOM(因为还没有渲染呢),若想在此阶段写DOM操作代码,可以使用nextTick函数回调,在mounted结束后立即执行;
beforeMount确立了挂载点,但是还没渲染DOM,所以依然获取不到DOM,属于重要的过渡阶段;
mountedDOM渲染完毕,可以访问DOM了;
beforeUpdate改变数据后其实先进去watch中的,之后进入此阶段,数据已更新,但是Dom还未更新,其实在这阶段生成了新的绑定vue实例数据的虚拟DOM结构;
updated生成virtual Dom,和之前的虚拟Dom进行differ算法对比,最小变动更新Dom完毕
beforeDestroy实例销毁之前,依然能正常访问数据和DOM;
destroyed销毁之后,数据能访问到,但是不能访问DOM了,改变数据不存在数据驱动;
总结:
beforeCreat:vue实例创建之前可以在此加入loding事件
created:loding可以消除了,实例已创建,可以在此发起ajax请求拉取数据,来做数据的进一步初始化
mounted:操作DOM,也可以发起后端请求,配合路由钩子做事情
updated:如果做统一数据处理,可以写上相应函数
beforeDestroy:离开前的确认框
nextTick:更新数据后立即操作DOM
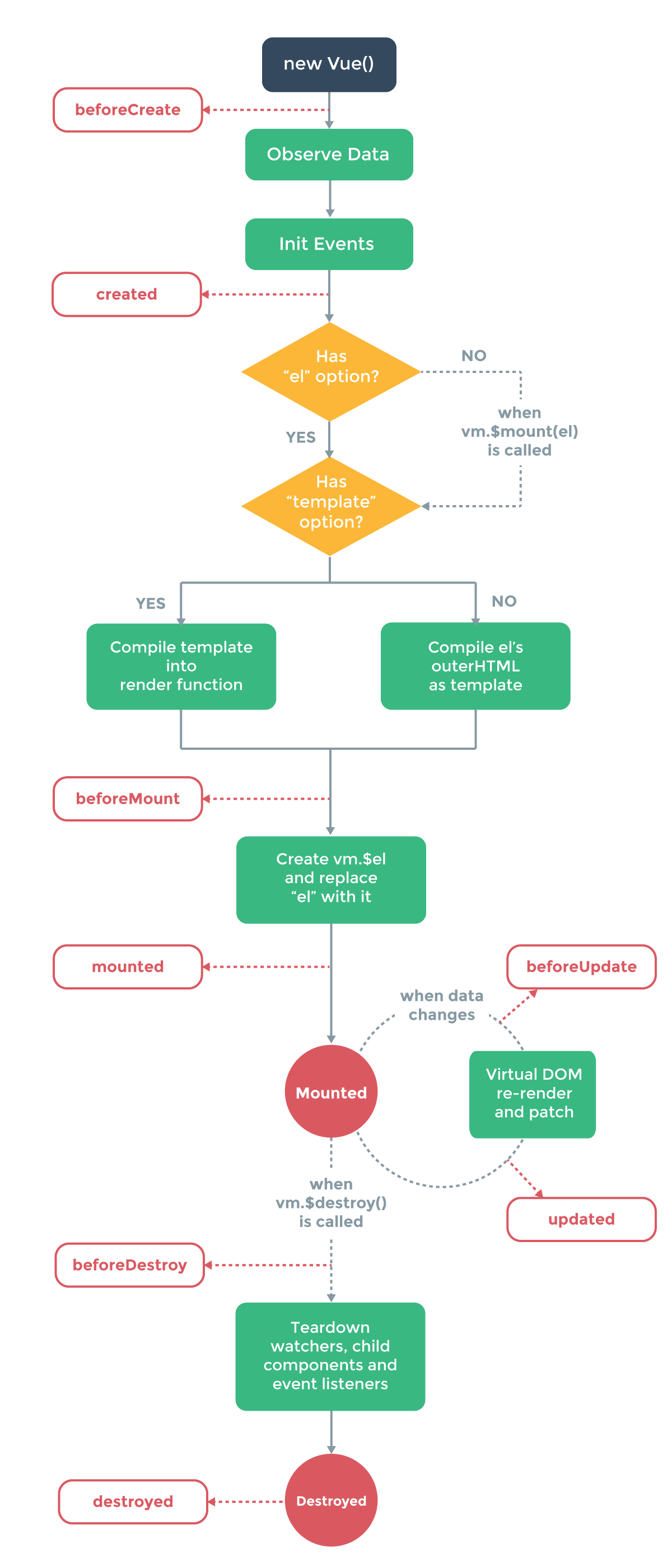
最后上个官方生命周期流程图,后面还有番外篇!
番外篇1:
除此之外做了些尝试
连续改变vue数据,例如点击按钮事件中连续两次更改data,更改代码如下:
1 | ... |
或者
1 | ... |
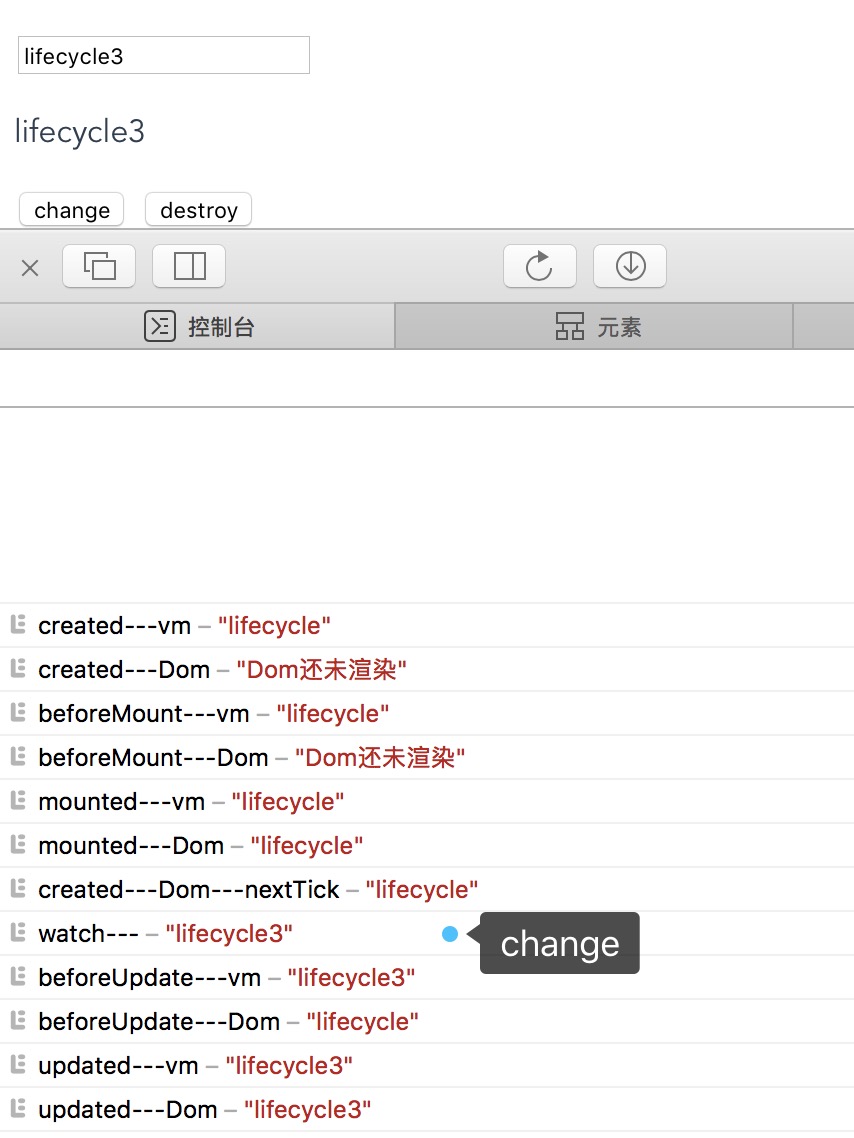
酱紫写只会触发一次beforeUpdate、updated,结果是最终结果
但是如果使用timeout,即便是执行时间写成0,也会触发两次beforeUpdate、updated,更改代码如下
1 | ... |
或者
1 | ... |
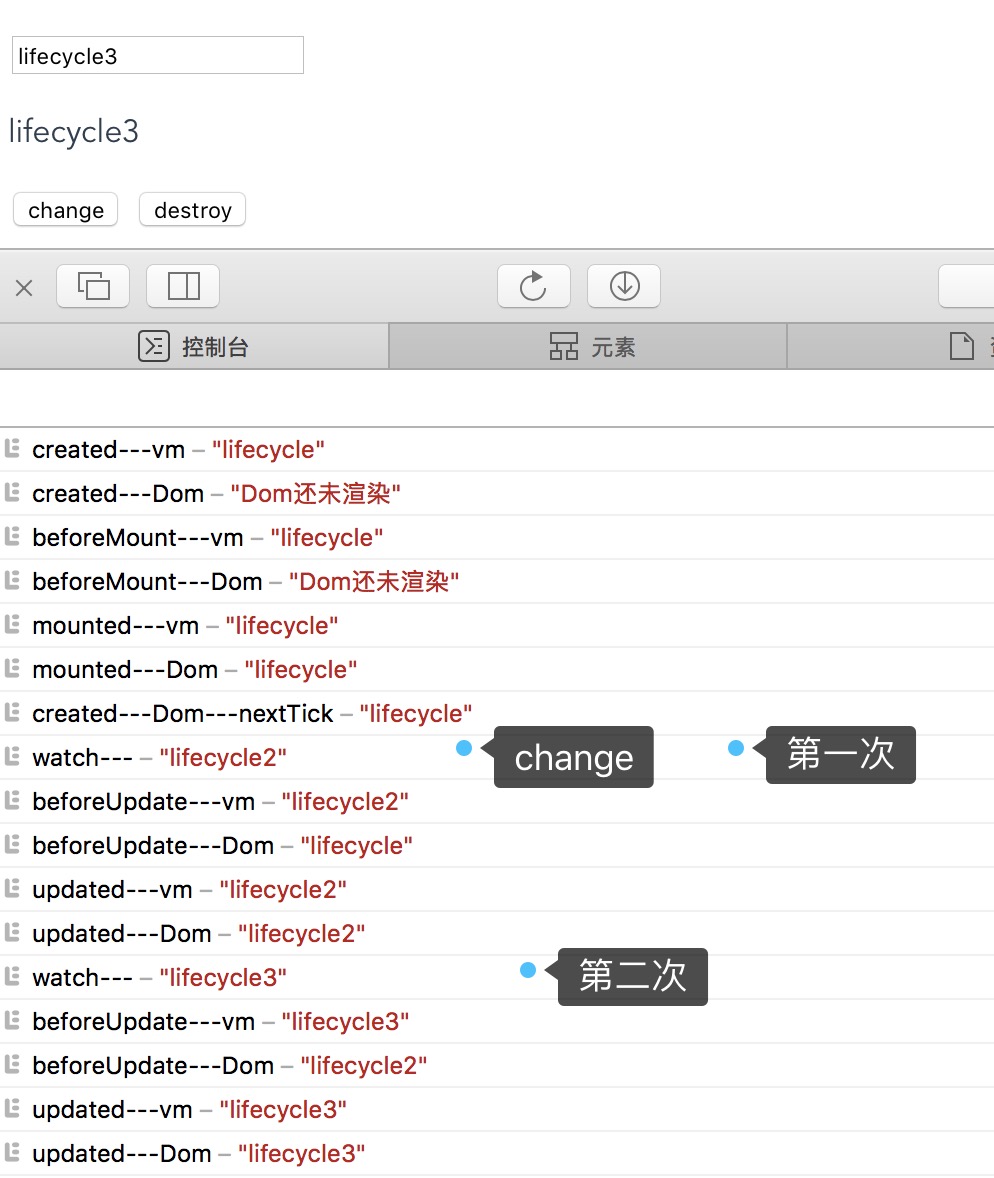
结果如下,跑了两次beforeUpdate、updated
在vue实例创建完成后,但是在
mounted结束之前,改变data数据
在created钩子函数中改,更改代码如下
1 | created: function () { |
结果如下
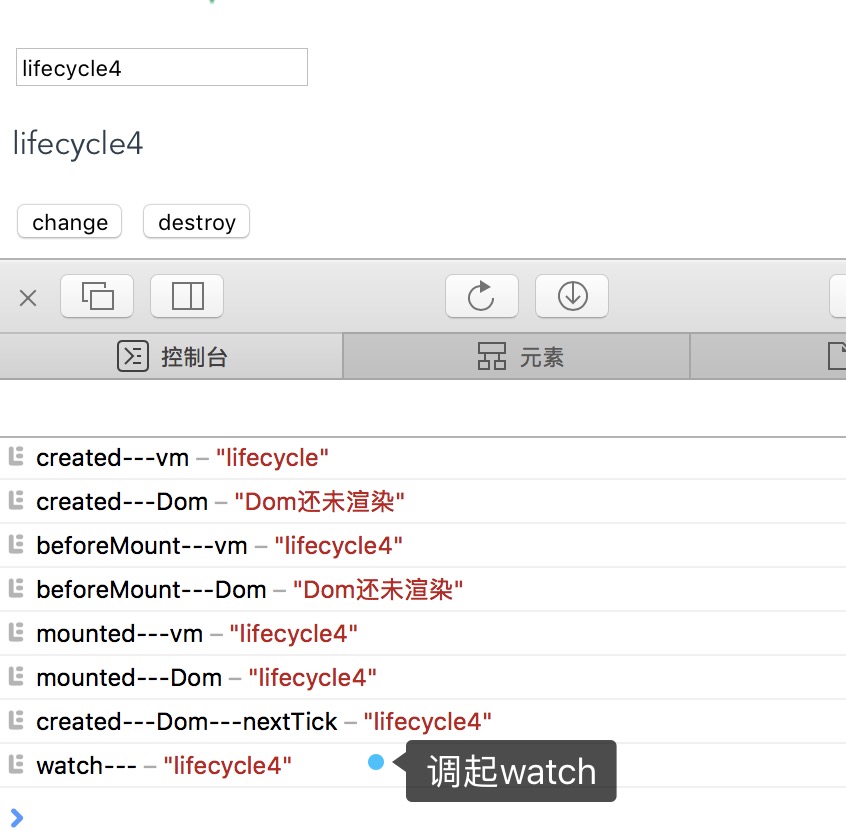
调用起watch是在意料之中,可能要注意的是调起它的时间,是在首次渲染结束后才会触发起watch,并且nextTick在其之前,所以说nextTick是在DOM完成后立即触发,这个立即很准确
但是如果在mounted中改变的话,还会触发beforeUpdate、updated,因为更新钩子函数就是在mounted完成后每次更改数据来重新渲染DOM时触发
番外篇2:
补充子组件生命周期和父组件生命周期的交叉情况
上面的代码其实是子组件,只是我完全独立的看待它本身的生命周期,现在在父组件中,添加一些钩子函数以及props,代码如下:
1 | <template> |
1 | <script> |
结果如下
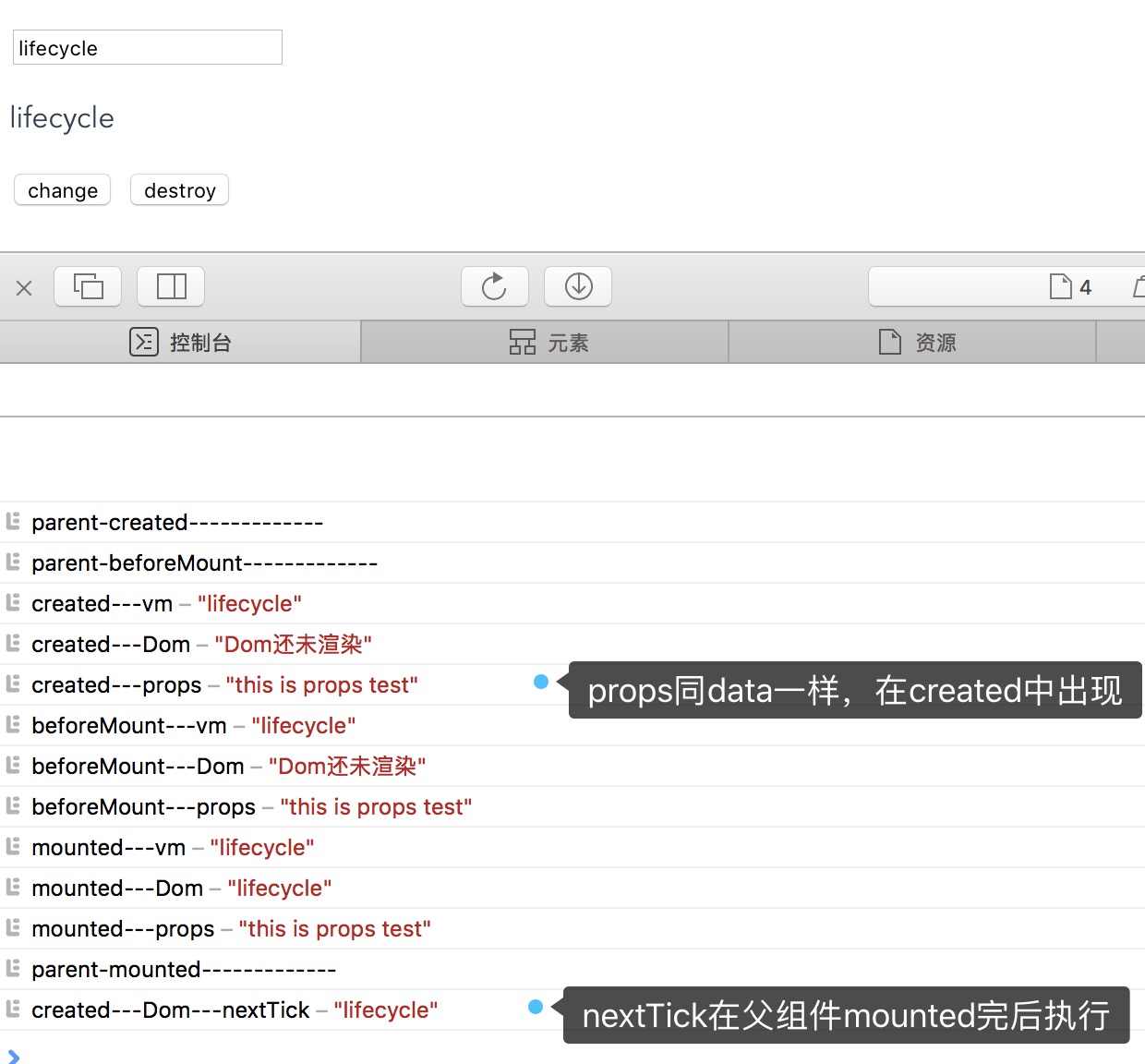
首先,props的出现周期和data是一样的,其次子组件的生命周期是在父组件的beforeMounted之后,父组件mounted之前执行完毕,并且nextTick在父组件mounted之后,即整个DOM渲染完之后再执行。
暂时这些,其他的研究可能需要在实际的开发中碰到了,以及深入的内容等到研究源代码的时候说吧~~